Staining unit; iSaCS
For
technicians and partly for sales managers!
 To stain a tissue automatically in the iSaCS, some
information is required. Because there are a lot of reagents in vials, the
identification of the vial (and so, the reagent) is required. Because the size
and the position of the tissue on the slide can vary and the reagents are often
very expensive, the required quantity of stain has to be calculated, and the
area of the specimen on the slide has to be known exactly. Furthermore, it is
important to know, how many reagents has to be used and for which tissues. All
this information is collected and handled by software and based on this
information, the staining process will be controlled.
To stain a tissue automatically in the iSaCS, some
information is required. Because there are a lot of reagents in vials, the
identification of the vial (and so, the reagent) is required. Because the size
and the position of the tissue on the slide can vary and the reagents are often
very expensive, the required quantity of stain has to be calculated, and the
area of the specimen on the slide has to be known exactly. Furthermore, it is
important to know, how many reagents has to be used and for which tissues. All
this information is collected and handled by software and based on this
information, the staining process will be controlled.
Overview
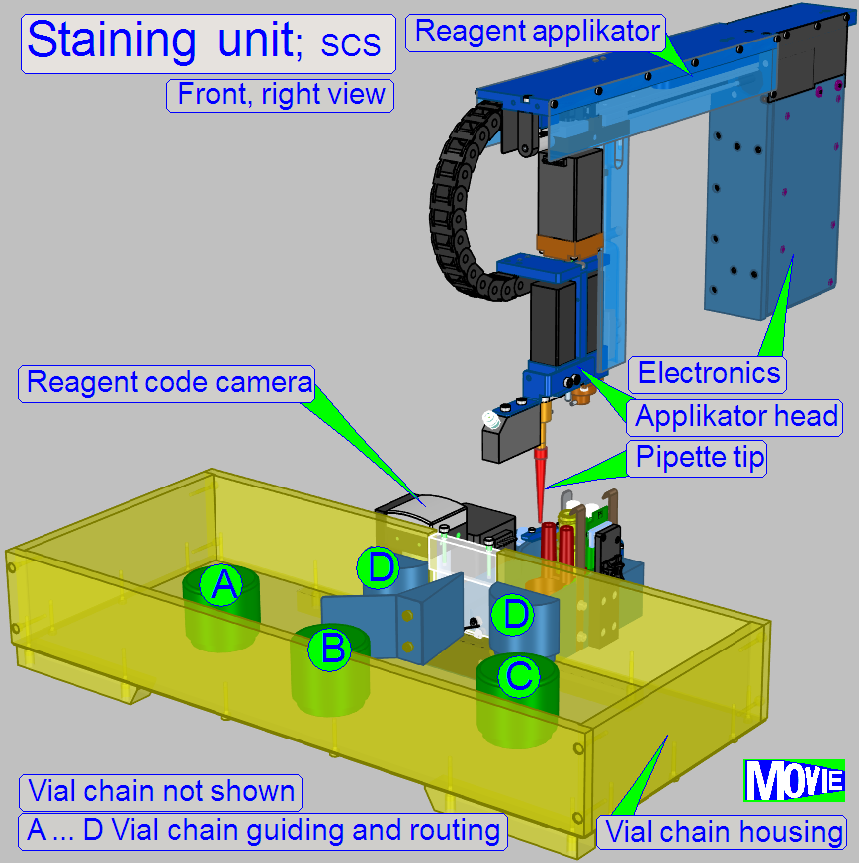 The
staining unit can be divided into three main parts.
The
staining unit can be divided into three main parts.
· Vial moving and selection
A stepper motor
driven transmission rotates a Maltese cross. The Maltese cross moves the vial
chain.
· Vial barcode capturing and
To select the required
stain (vial) the position of the vial in the chain is required. Assigning the
stain to the position in the vial chain is performed via the vial’s barcode and
software.
· Application of the stain (reagent)
By filling the
appropriate pipette tip with the assigned reagent and moving it over the sample
area, stain will be applied onto the specimen area.
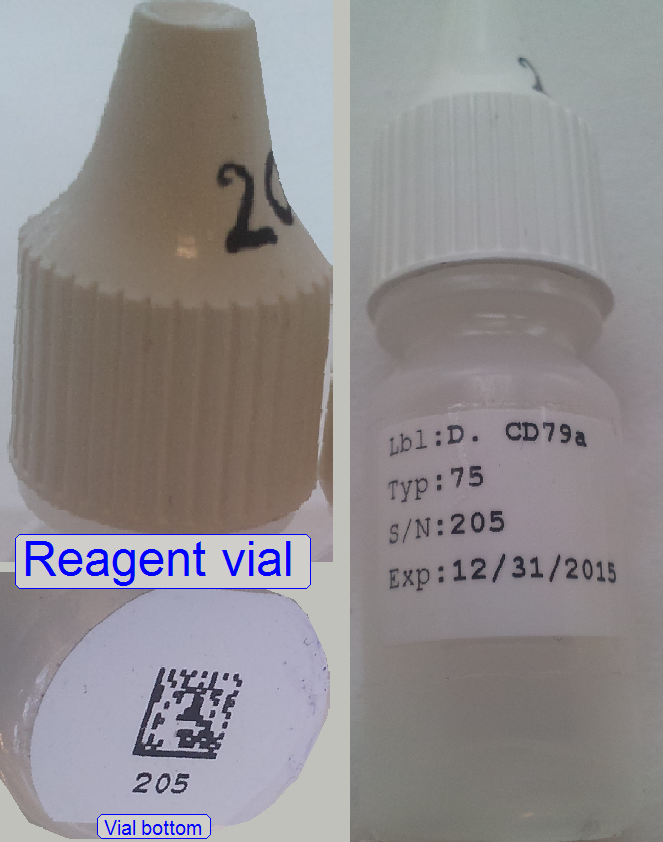
Reagent vials are inserted into the vial chain manually
when the whole equipment is shut off.
Every vial has a matrix code on the bottom to identify
the actual vial.
The code includes name, quantity, expiry date and
other information.
· Required
parameters and values are collected in the process control table.
For basics about fluorescent scan techniques, staining, fluorophores and
others
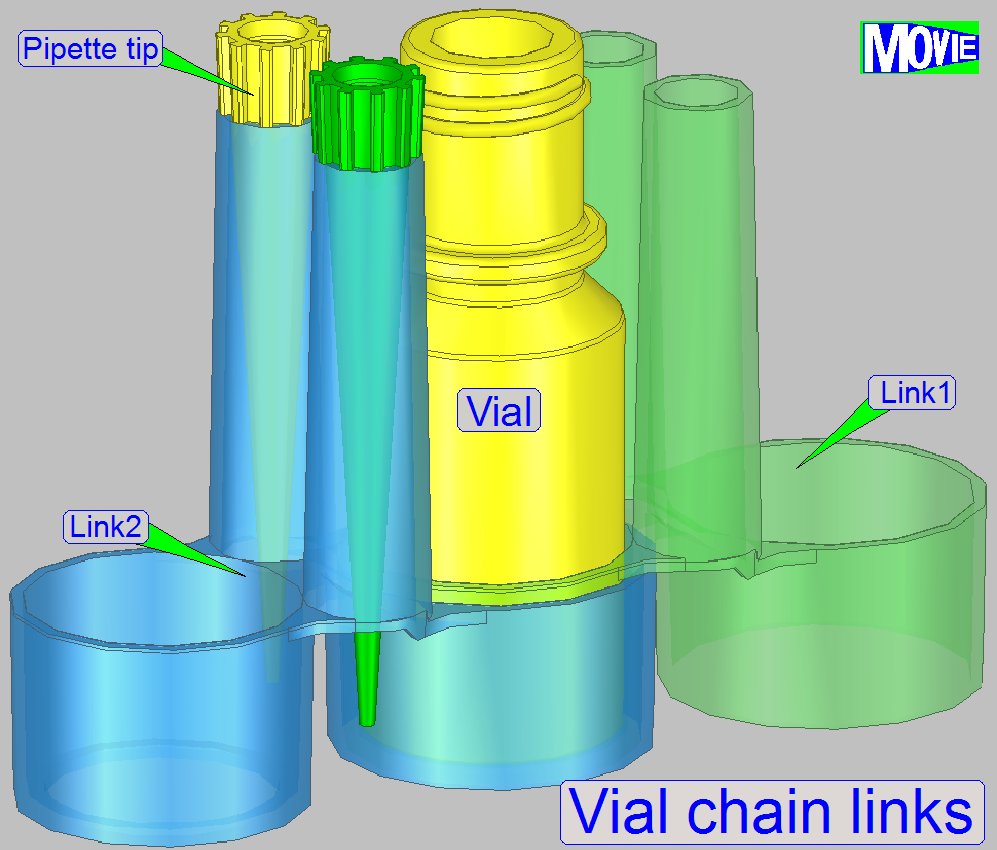
A chain link contains two pipette tip holder and two vial
acceptor shapes, different in diameters; so shapes of two vial acceptors are
fitting each other.
Pipette
tip
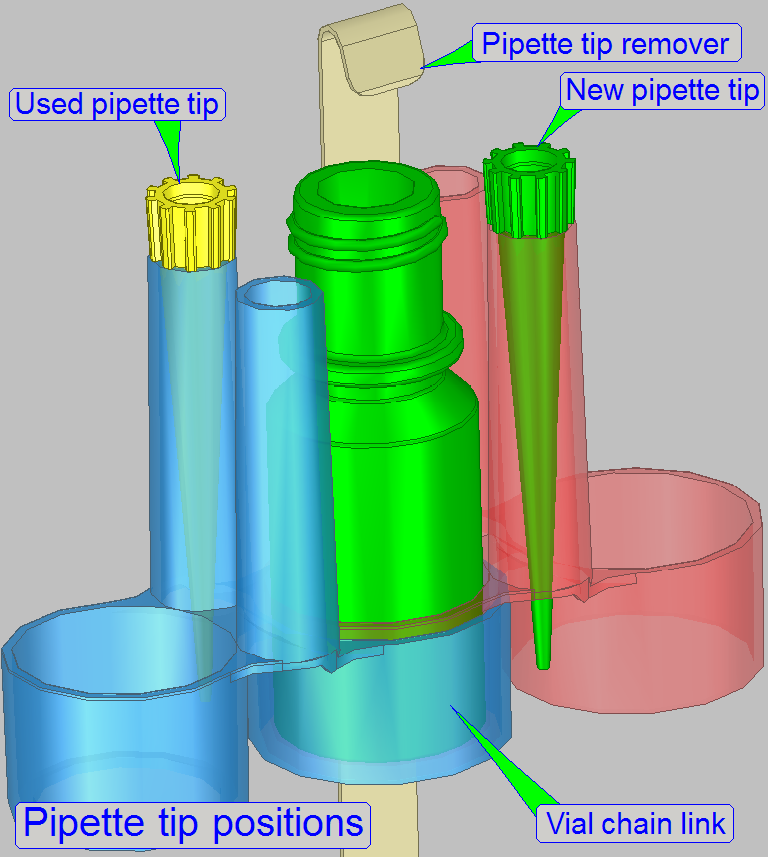 The system is able to differentiate between 2 pipette tips;
the used pipette tip and the new pipette tip.
The system is able to differentiate between 2 pipette tips;
the used pipette tip and the new pipette tip.
If the reagent vial was exchanged with a new vial of
the same reagent or by a different reagent vial, the pipette has to be placed
into the position of the “New pipette tip” as shown.
· The
pipette tip acceptor takes the tip at first time from this position.
· After
the stain applying process is finished, the pipette tip will be stored in the
position ‘Used pipette tip’.
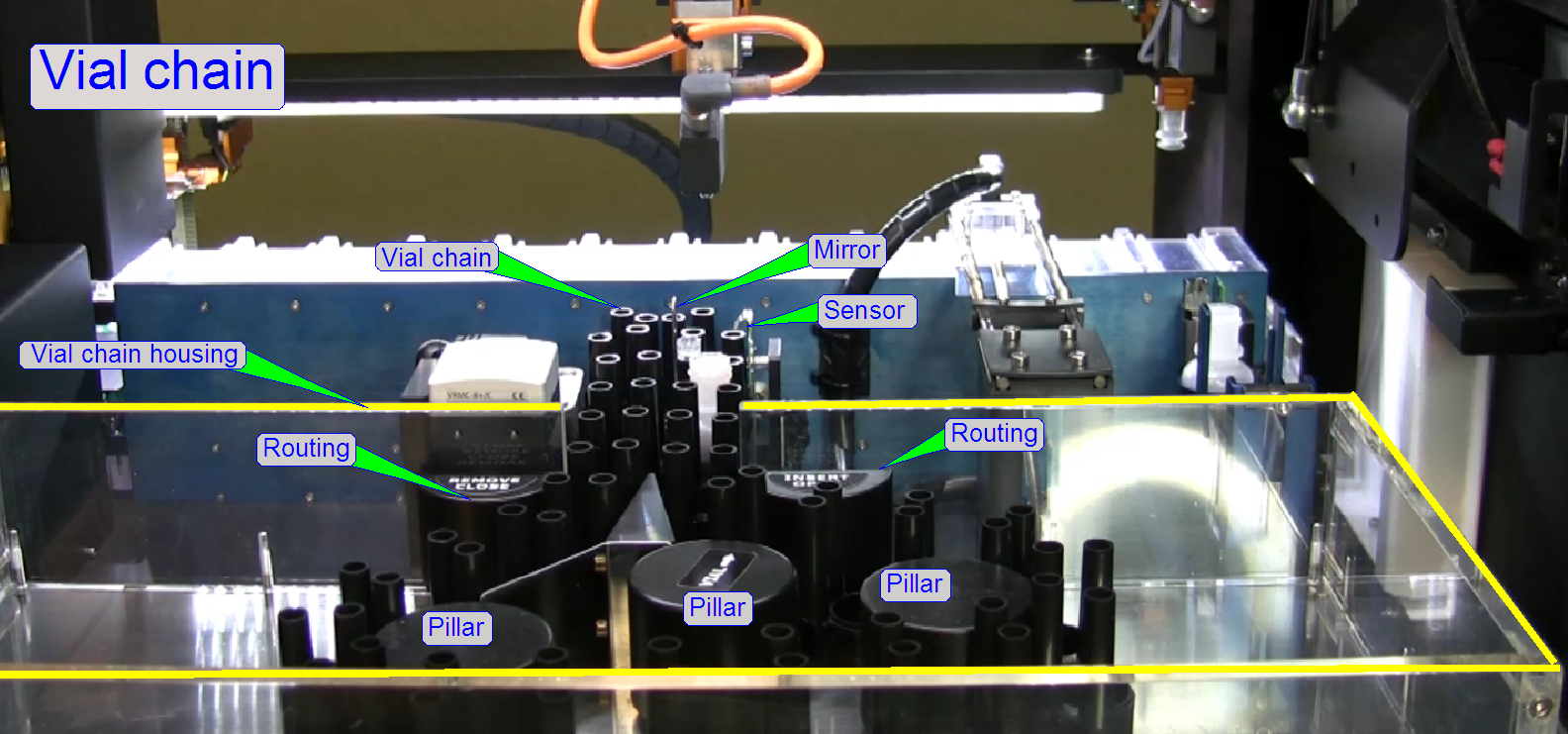 By
implementing of links into the vial chain, the number of available reagent
vials may be increased.
By
implementing of links into the vial chain, the number of available reagent
vials may be increased.
· Maximal
number of vials in the chain: 40
By dismounting of chain links from the vial chain, the
number of available reagent vials may be decreased.
· Minimal
number of vials in the chain: 17
Sensor
The IR-sensor
beside the pipette tip is used to detect
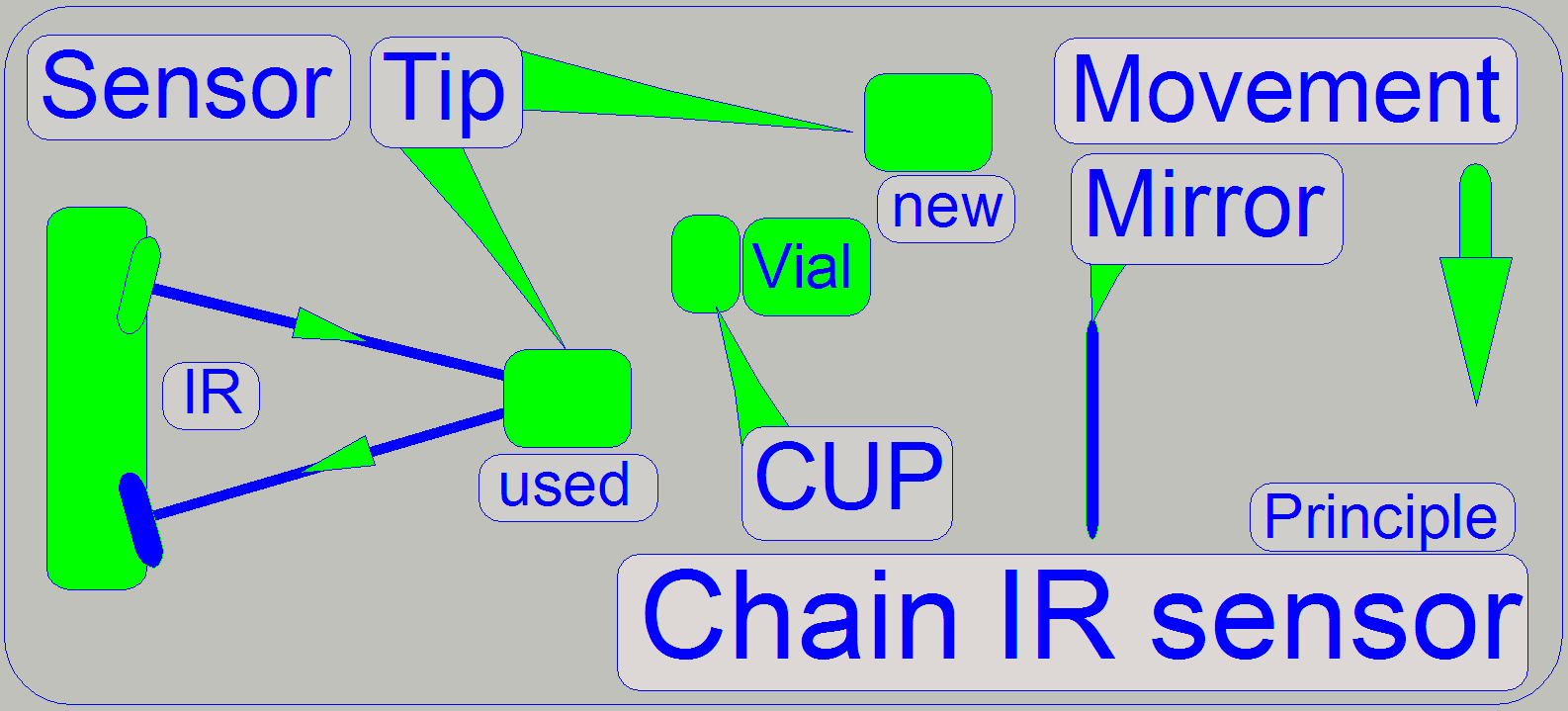
· Presence
of a used pipette tip
· Presence
of a new pipette tip
· Presence
of the vial cup
· Presence
of the vial
The components are moving in front of the sensor. The
IR beam of the sensor will be reflected on the components with different
intensity, depending on the distance between the particular component and the
sensor. By calibrating expected distances, the presence of expected parts can
be distinguished.
As the vial chain moves, the different components pass
the sensor. The nearest passing component is the used pipette tip, then the
vial (with or without cap) and the farthest is the new pipette tip.
If any component is not present, the mirror is used to
reflect the IR beam and so the software knows in conjunction with the position
of the vial chain, which component is missed.
Vial
chain housing
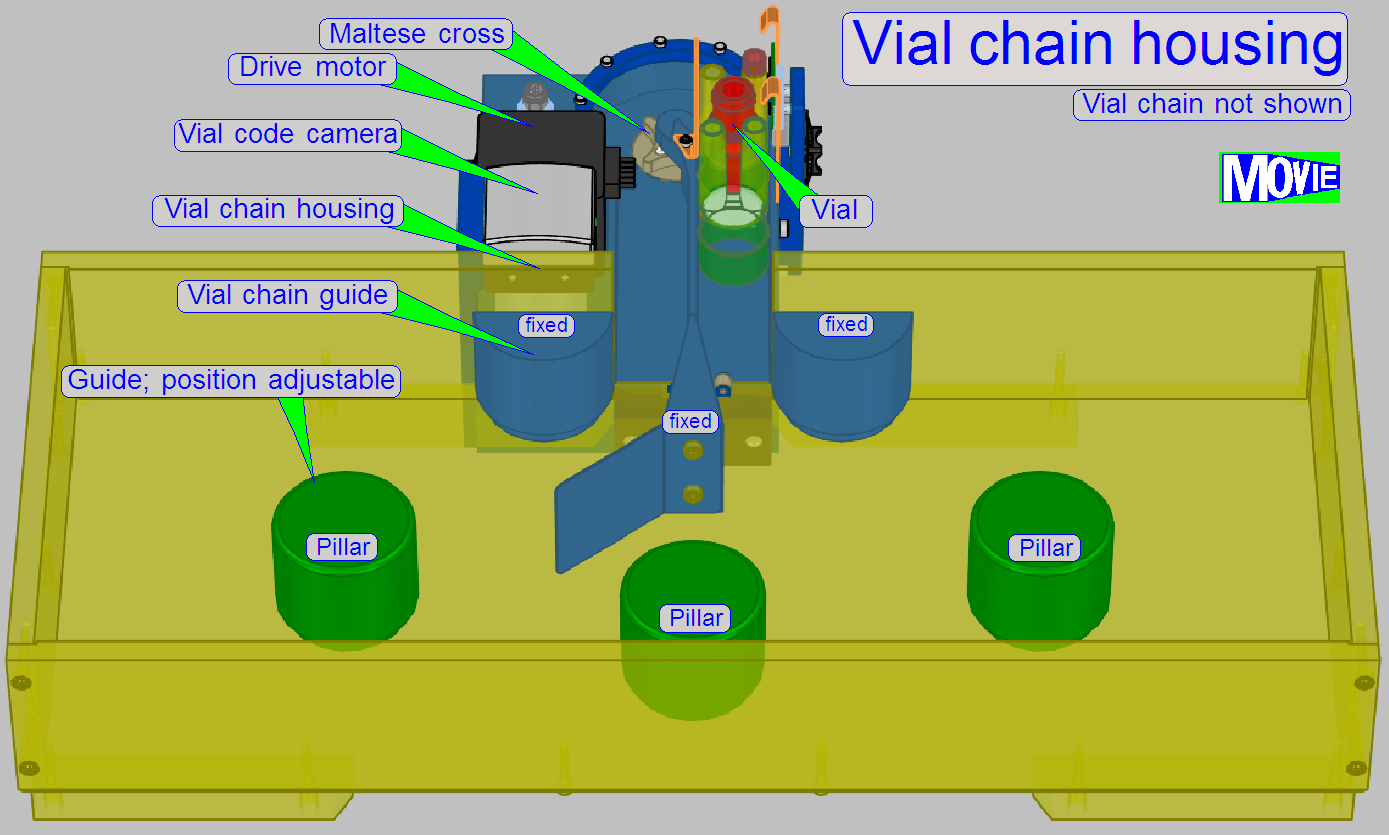 The housing covers the vial chain and protects
the reagents from dust.
The housing covers the vial chain and protects
the reagents from dust.
· In the
housing, the vial chain will be routed.
To increase or decrease the number of links in the
chain three position-able vial chain guide pillars are situated. By adjusting
their position, a smooth movement of the chain links can be reached.
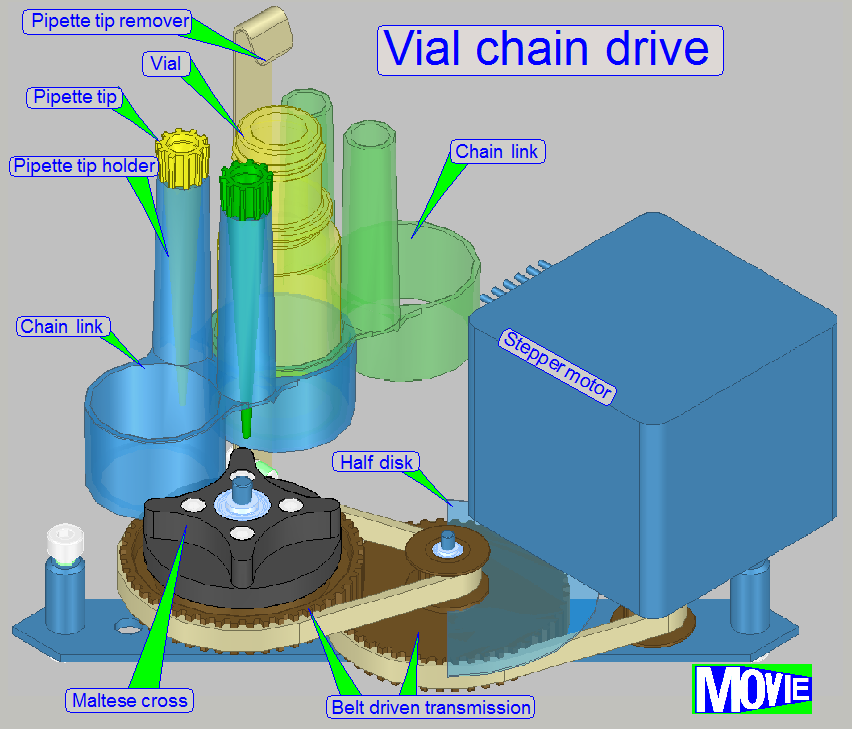 The
stepper motor drives a belt driven transmission
The
stepper motor drives a belt driven transmission
· On
the first transmission wheel the “Half disc” for home detection is mounted.
· On the
second transmission wheel the Maltese cross is mounted.
· By moving
the stepper motor's rotor a defined number of steps, the vial is changed by
exactly 1 position
Vial
code capturing
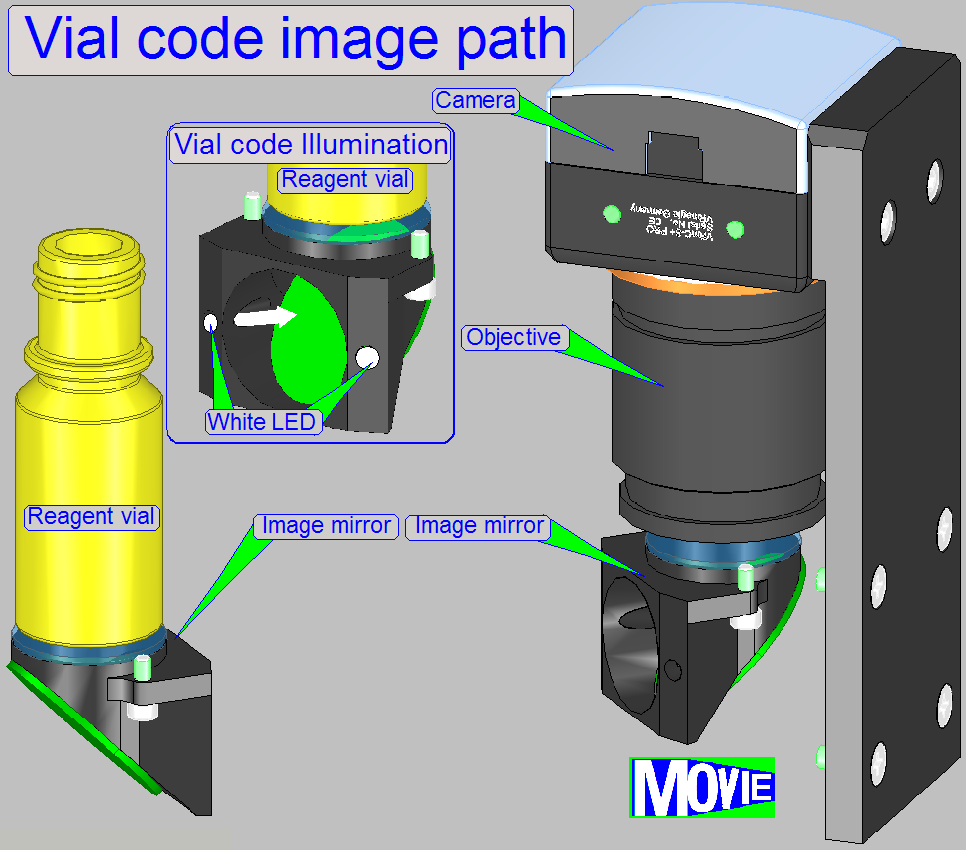
Main components are
· Barcode
on vial’s bottom
· Illumination
of the vial’s bottom
· Mirrors,
to reflect the image path to the objective
· Objective
· Camera
By illuminating the vial’s bottom by 2 white LEDs the
code of the vial is visible.
· If the
correct vial position is reached, the camera makes an image of the vial bottom;
the image is send to the barcode analyzing software.
The barcode is used to find the vials position inside
the chain and to identify the reagent, so the reagent’s parameters are known.
· The
sequence of the vials in the chain is stored in the vials chain table.
Reagent code camera
 The camera makes an image of the vial’s bottom
The camera makes an image of the vial’s bottom
· By
analyzing the barcode, the reagent name and it’s parameters are known
· The position
of the reagent in sequence inside the chain is recognized and an item in the
reagent position table is updated.
Reagent code objective
·
Tamron M118FM25 (for vial
barcode)
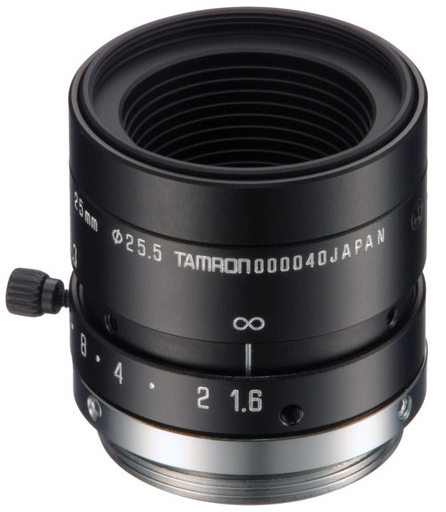

The barcode view objective is a Tamron M118FM25 Megapixel Fixed-focal
Industrial Lens (25mm).
·
Delivers optimum performance in the center and in the
edges
·
Anti-vibration construction
Specifications
|
Tamron M118FM25 |
|
|
Parameter |
Value |
|
Imager Size |
1/1.8" |
|
|
C |
|
Focal Length |
25mm |
|
Aperture |
1.6-16 |
|
Angle of View (HxV) |
1/1.8":
16.6 x 12.5° |
|
1/2":
14.6 x 11° |
|
|
1/3":
11 x 8.2° |
|
|
Distortion |
TV
Distortion: Less than -0.2% |
|
Minimum Object Distance (M.O.D.) |
0.1m ~ ∞
|
|
Focus Operation |
Manual
with lock |
|
Iris Operation |
Manual
with lock |
|
Filter Size |
M25.5
P=0.5mm |
|
Back Focus |
(in air) |
|
Operating Temperature |
14 - |
|
Dimensions (Diam. x L) |
1.1 x
1.4" (29 x 24mm) |
|
Weight |
|
|
Suitable for |
FA
(Factory Automation) and Machine
Vision application |
|
Immersion depth |
4.6mm |
|
Resolution |
2.23 MPix |
Introduction
In reality, the real reagent applicator is the pipette
tip itself.
The unit, named as “Reagent applicator” is used to
control the pipette tip’s movement and actions.
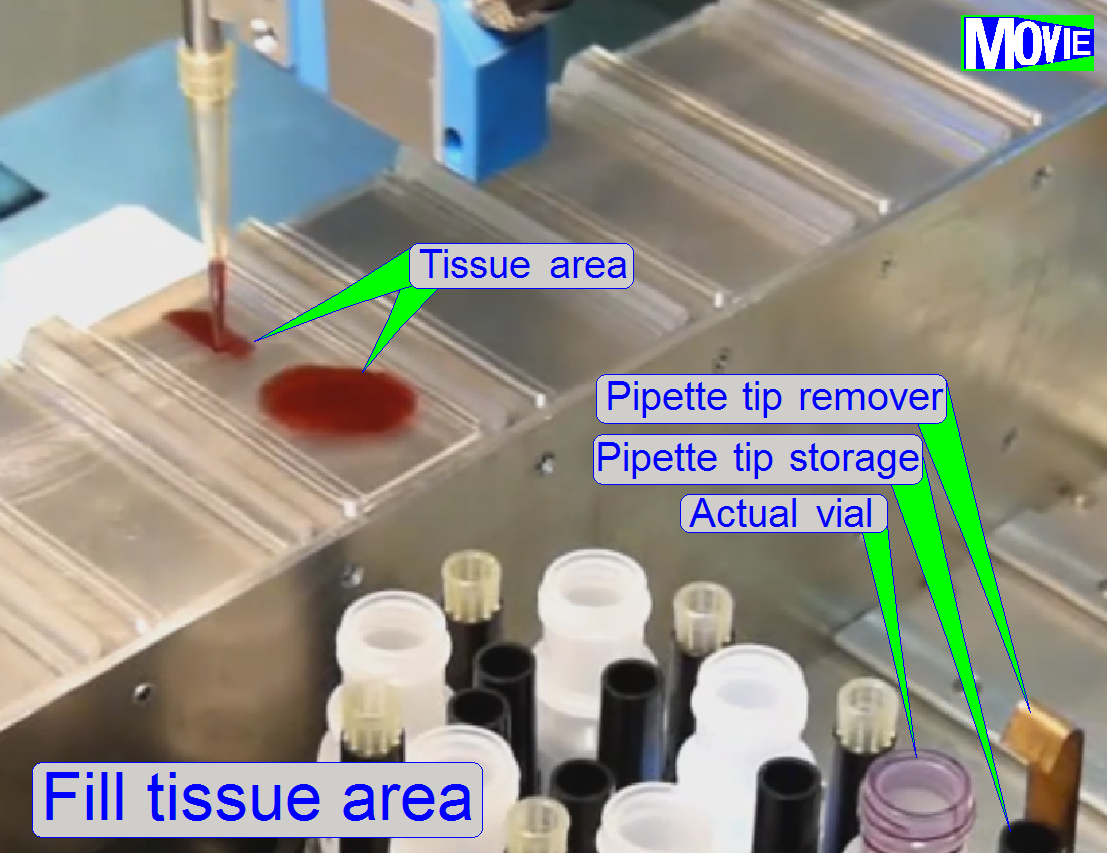 We assume,
the slide is already placed in the manipulation bay 7
We assume,
the slide is already placed in the manipulation bay 7
The quantity of reagent for the tissue is known
Pipette tip actions in sequence
· Move the
pipette tip acceptor to the pipette tip store position and take the pipette
tip.
· Move
the pipette tip over the actual reagent vial.
· Define
the immersing deepness of the pipette tip, depending on the required quantity
of reagent.
· Insert
the pipette tip into the vial.
· Filling
the pipette tip with the required quantity of reagent; create a defined vacuum.
· Move
the pipette tip out of the vial.
· Move
the pipette tip over the manipulation bay 7.
· Move
the pipette tip to the start point of the tissue.
· Fill
the sample area with stain; hereby defined pressure will be created onto the
liquid in the pipette tip. The pipette tip moves on a meandering course.
· If the
slide contains several sample areas, each area will be filled separately.
· If the
sample fill process is finished, move the pipette tip to its storage position.
· Remove
the pipette tip and place it in its store
· 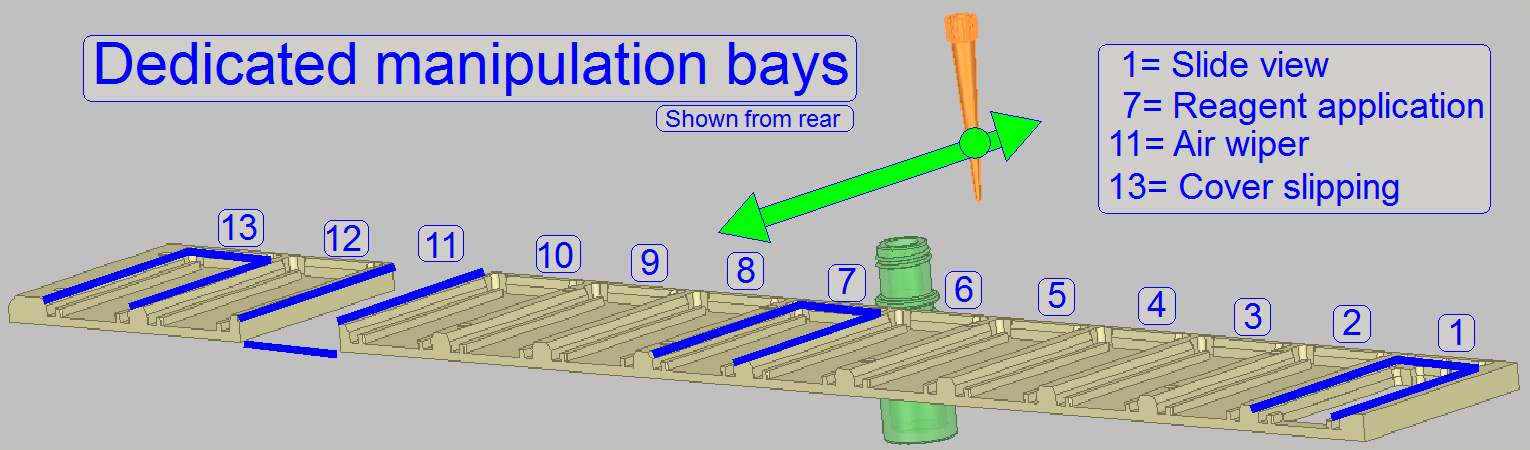 The dedicated application bay for staining is the bay 7.
The dedicated application bay for staining is the bay 7.
The movements of the pipette tip are executed with the
“Reagent applicator”
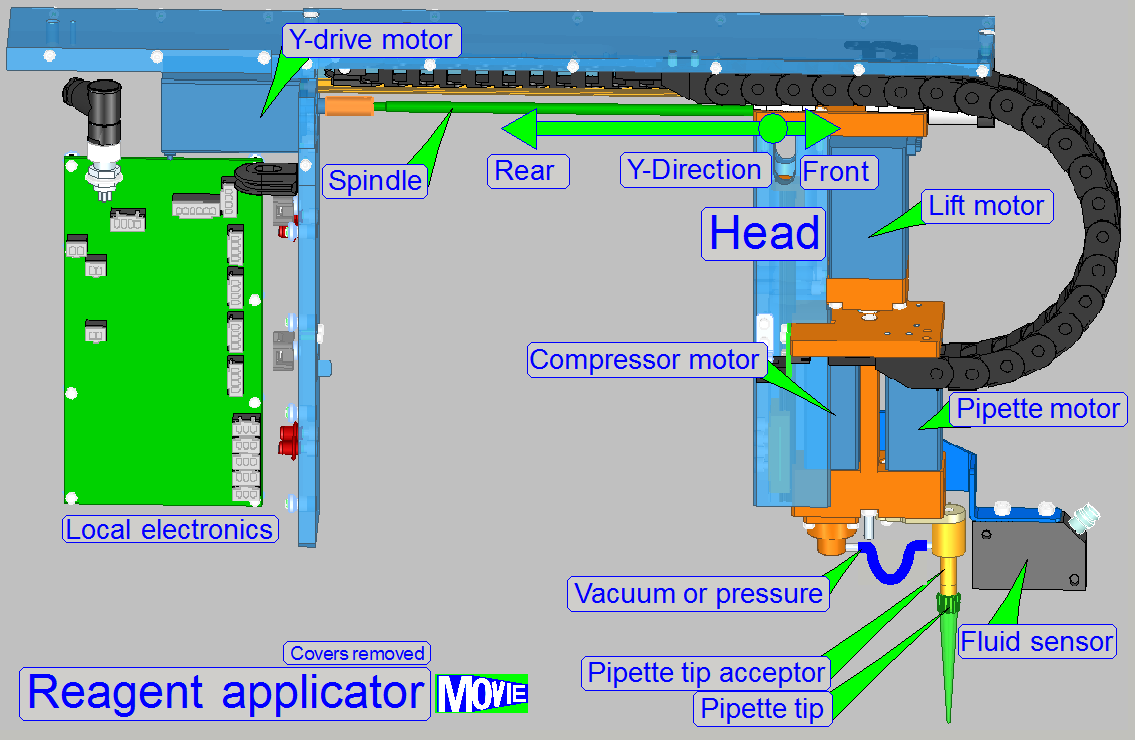
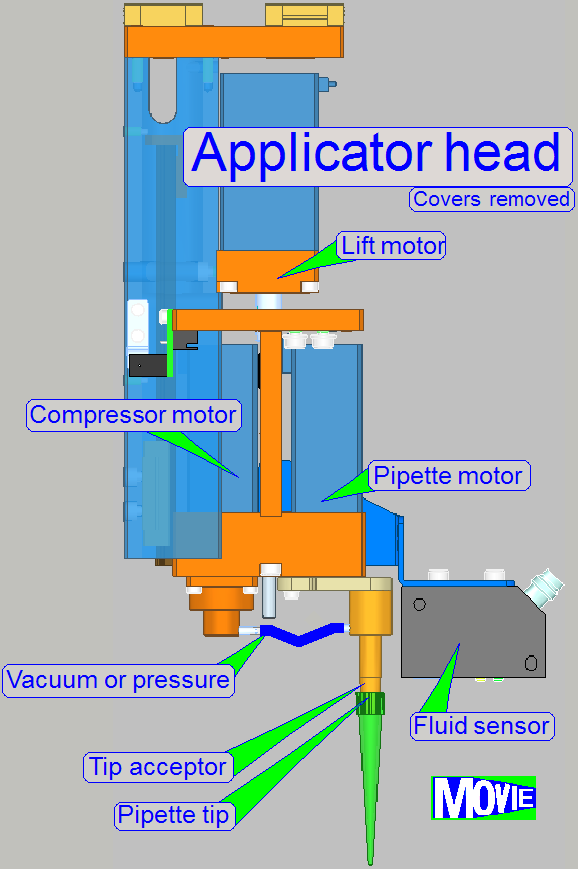
The applicator head controls the pipette tip; main
components are
· Lift
motor; the moveable part of the applicator head and so, the pipette tip, is
moved in Z-direction
· Pipette tip mover with tip acceptor;
moves the pipette tip on the width of the slide, in the X-direction.
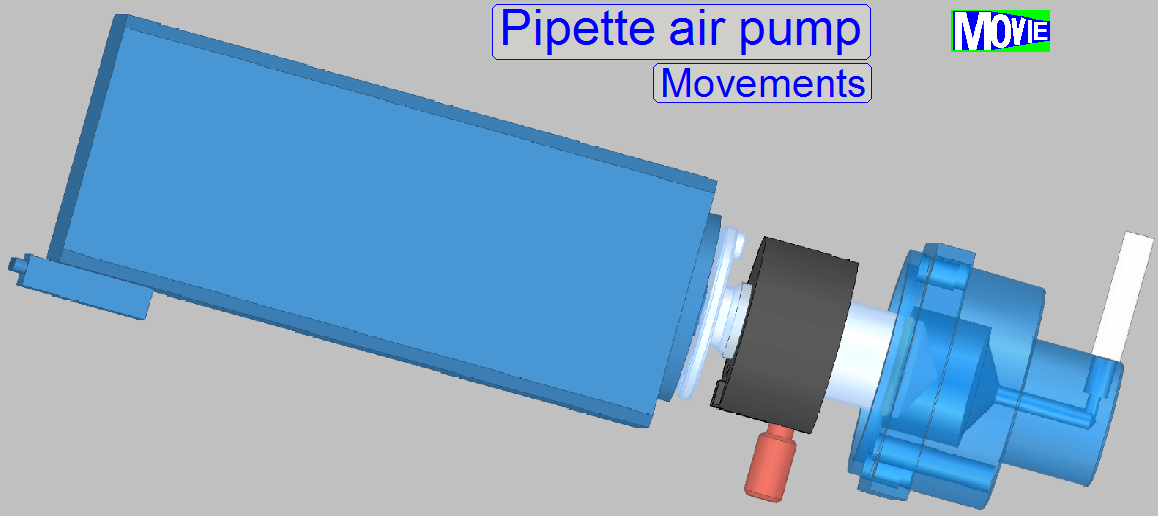
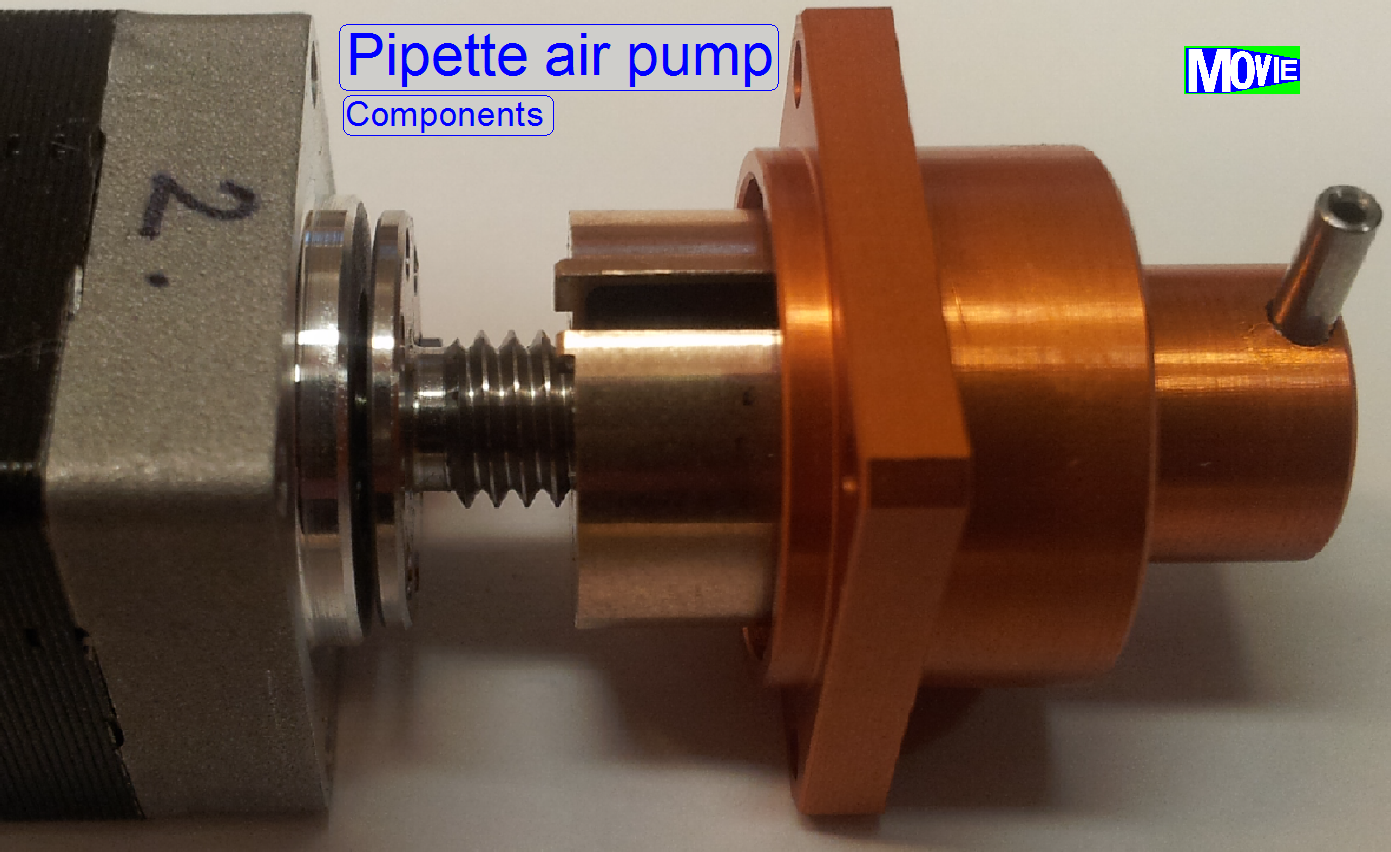
· Compressor
with motor; the ‘Air pump’
· Fluid
level sensor
· Pipette
tip; exchangeable
· The
air pump creates a defined vacuum to fill the pipette tip with reagent and
· Creates
a defined pressure onto the reagent in the pipette tip to apply the stain.
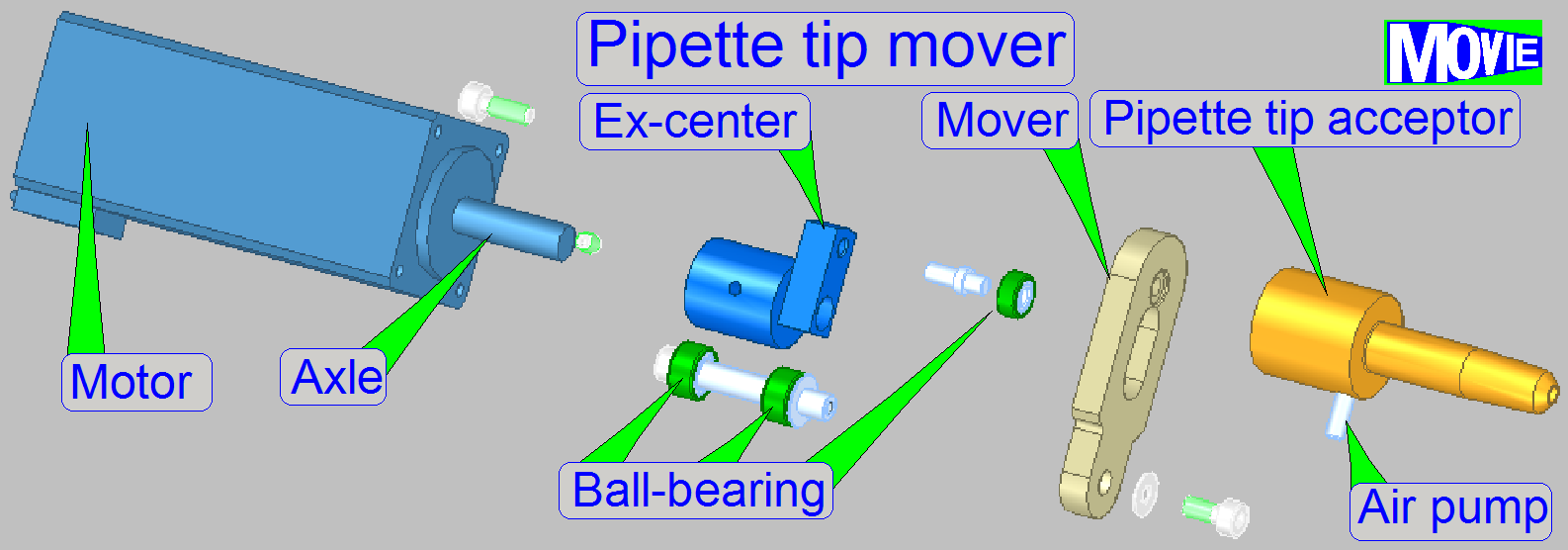 The
“Pipette tip mover“ executes the movement of the pipette tip in the
mathematical X-direction (the width of the slide; nominal 26mm).
The
“Pipette tip mover“ executes the movement of the pipette tip in the
mathematical X-direction (the width of the slide; nominal 26mm).
· The mover
reaches also the new and used tip storage position to accept and release the
pipette tip.